“If there was something excellent to be used as a remedy then it is cupping (hijama).”
Saheeh Sunan abi Dawud (3857), Saheeh Sunan ibn Maajah (3476)
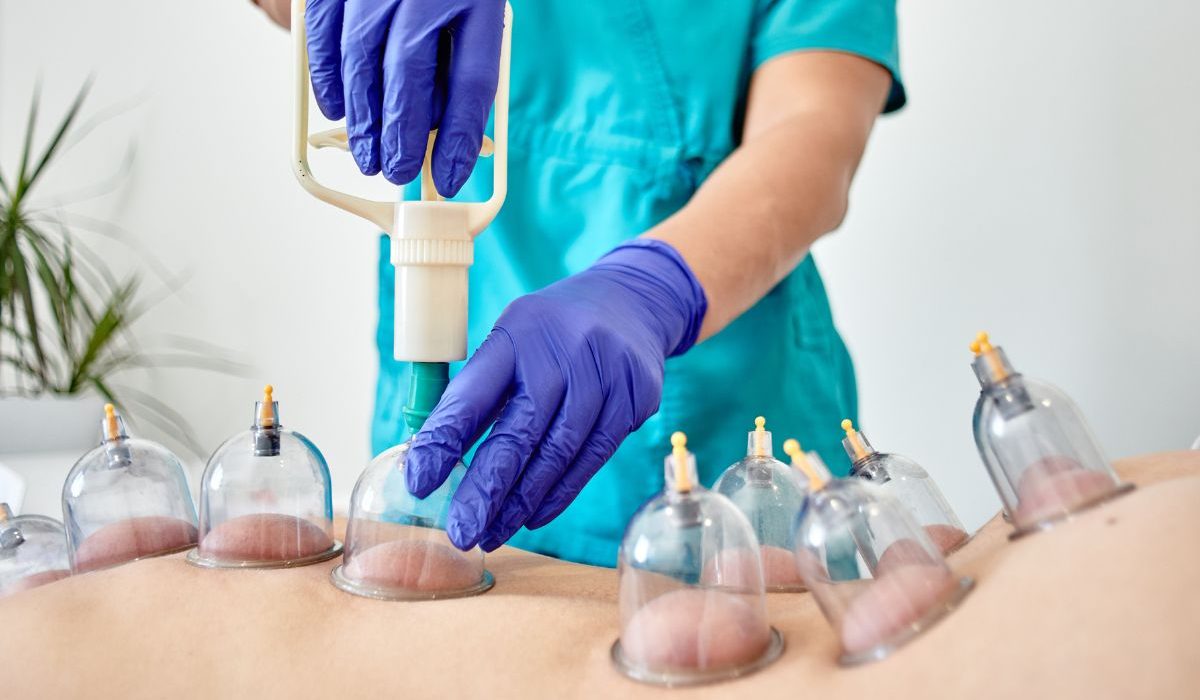
In the realm of alternative medicine, Hijama therapy emerges as a time-honored practice with profound implications for pain management. Originating from traditional Islamic medicine, this therapeutic technique involves the application of cups to specific points on the body, facilitating healing through controlled suction and bloodletting. While its roots may be ancient, modern research and anecdotal evidence alike are increasingly validating its efficacy in alleviating various forms of pain.
Understanding Hijama Therapy:
Hijama, also known as cupping therapy, operates on the principle of enhancing blood flow to affected areas, thereby promoting healing and relieving pain. Practitioners typically use cups to create a vacuum effect on the skin, drawing blood to the surface and stimulating the circulatory system. This process is believed to remove toxins, improve oxygenation, and encourage the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Applications in Pain Management:
- Musculoskeletal Pain: Hijama therapy is particularly renowned for its effectiveness in treating musculoskeletal pain such as back pain, joint pain, and muscle stiffness. By targeting trigger points and releasing tension, it offers relief comparable to conventional therapies but with potentially fewer side effects.
- Headaches and Migraines: Many individuals suffering from chronic headaches and migraines have reported significant relief after undergoing Hijama therapy. The improved blood circulation and release of muscle tension around the neck and shoulders are believed to contribute to this relief.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes and sports enthusiasts often turn to Hijama therapy to accelerate recovery from injuries, reduce inflammation, and manage pain associated with strenuous physical activity.
- Chronic Pain Conditions: Conditions such as fibromyalgia and arthritis, which pose ongoing challenges for conventional medicine, may find complementary relief through Hijama therapy. It addresses both localized pain and systemic inflammation, offering a holistic approach to managing chronic pain.